Near miss reporting plays a crucial role in ensuring patient safety within healthcare settings. It allows healthcare professionals to identify potential risks and hazards, leading to proactive measures that can prevent accidents and adverse events. Understanding the significance of near miss reporting, QUASR conducted a survey during the APHM Conference and Exhibition 2023 to gain valuable insights into the current state of near miss reporting in healthcare. Let’s delve into the objectives of the survey and the methodology employed to collect data.
Table of Contents
Objectives of the Survey
The primary objective of the survey conducted by QUASR was to assess the level of awareness, barriers and ways to encourage near miss reporting in healthcare organizations across Malaysia. By obtaining first-hand insights from professionals working in various roles within the healthcare industry, the survey aimed to gauge the current state of near miss reporting practices.
Methodology
The respondents encompassed 115 delegates with a diverse range of roles, including CEOs, COOs, CNOs, GMs/Operations Managers, HODs, Quality/HR/Procurement Managers, Nursing Managers, Nurses and IT Managers. This well-distributed profile ensured a comprehensive understanding of near miss reporting practices from different perspectives.
To facilitate data collection, respondents were provided with a convenient and efficient online form. They could access the form by scanning a QR code provided at the QUASR booth. This allowed for a streamlined and user-friendly experience, ensuring a higher response rate and more accurate data.
By employing this methodology, QUASR gathered valuable insights into the current awareness levels, barriers, and potential initiatives to promote near miss reporting within healthcare organizations. Let’s explore the survey results and their implications.
Awareness Levels
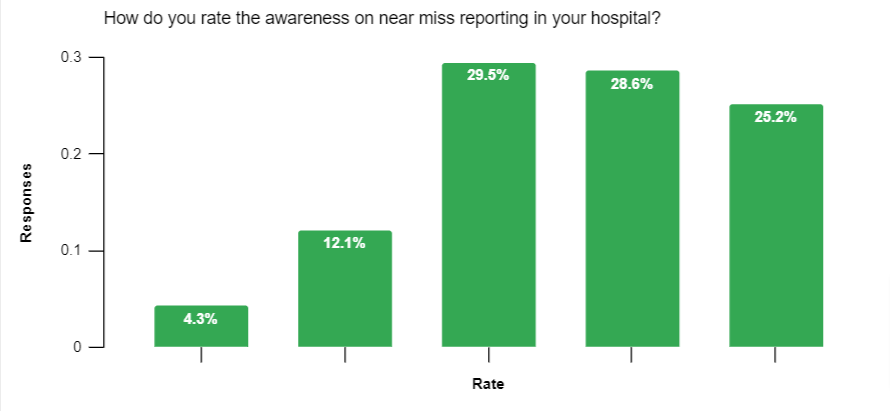
We used a rating scale of 1 to 5 to assess the awareness levels of near miss reporting in healthcare organizations where 1 indicated low levels and awareness and 5 indicates a high level of awareness. Here’s a breakdown of the results and their implications:
- 25.2% of respondents rated the awareness level as 5, indicating a high level of awareness.
- 28.6% of respondents rated the awareness level as 4, showing a substantial understanding of near miss reporting.
- 29.5% of respondents gave a rating of 3, suggesting moderate awareness.
- 12.1% of respondents rated the awareness level as 2, indicating a lower level of awareness.
- 4.3% of respondents gave a rating of 1, representing a significantly low level of awareness.
While the overall awareness level was relatively high, the presence of lower ratings highlights the need for continuous improvement and education in near miss reporting practices.
Understanding these rating categories helps organizations tailor their strategies to enhance near miss reporting culture.
Barriers to Near Miss Reporting
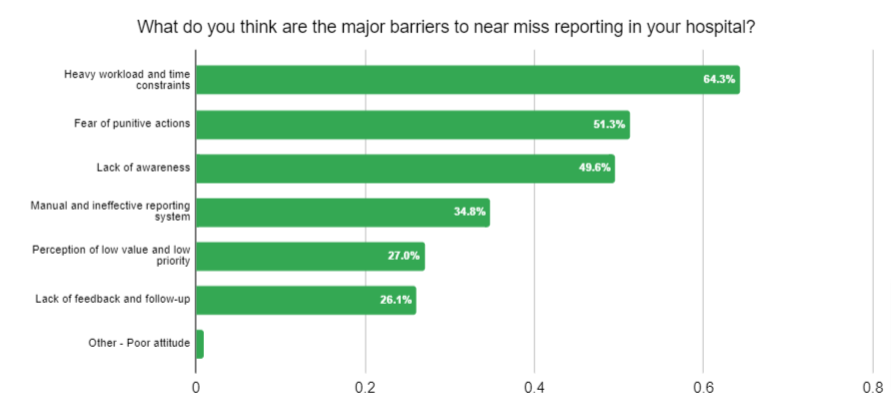
Our survey shed light on the major barriers that healthcare organizations face in implementing effective near miss reporting. Let’s delve into each barrier, backed by results from the survey, and explore their impact on near miss reporting culture and patient safety.
- Heavy Workload and Time Constraints: The survey results revealed that a substantial majority of respondents (64.3%) faced heavy workload and time constraints, which hinder their ability to dedicate time to near miss reporting. Overburdened staff may prioritize immediate tasks over reporting, thereby impeding the identification and resolution of potential risks.
- Fear of Punitive Actions: A significant percentage of respondents (51.3%) reported fear of punitive actions as a barrier. When healthcare professionals are afraid of facing consequences for reporting near misses, they may choose to remain silent, leading to underreporting and missed opportunities for learning and improvement.
- Lack of Awareness: A substantial portion of respondents (49.6%) cited a lack of awareness as a barrier to near miss reporting. This indicates a need for increased education and communication about the importance of near miss reporting, its potential impact on patient safety, and the benefits of a proactive reporting culture.
- Manual and Ineffective Reporting Systems: A significant number of respondents (34.8%) faced challenges with manual and ineffective reporting systems. Outdated or inefficient systems can discourage timely reporting and hinder the analysis of near misses, potentially compromising patient safety.
- Perception of Low Value and Low Priority: Approximately 27.0% of respondents expressed that near miss reporting is perceived as having low value and low priority within their organizations. This perception can lead to a culture where near miss incidents are not taken seriously, thereby missing out on opportunities to identify and mitigate risks that could impact patient safety.
- Lack of Feedback and Follow-up: A significant number of respondents (26.1%) highlighted the lack of feedback and follow-up as a barrier. Without proper feedback and follow-up mechanisms, healthcare professionals may perceive near miss reporting as a futile exercise, resulting in decreased motivation to report incidents in the future.
- Poor Attitude: Although a small percentage (0.9%) of respondents mentioned a poor attitude as a barrier, it is still crucial to address. A negative attitude towards near miss reporting can discourage healthcare professionals from actively reporting incidents, hindering the identification and prevention of potential risks.
These barriers significantly impact near miss reporting culture and patient safety within healthcare organizations. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that includes addressing workload concerns, fostering a no-blame culture, raising awareness about the value of reporting, implementing user-friendly reporting systems, establishing feedback mechanisms and promoting a positive reporting attitude.
Proposed Initiatives for Management
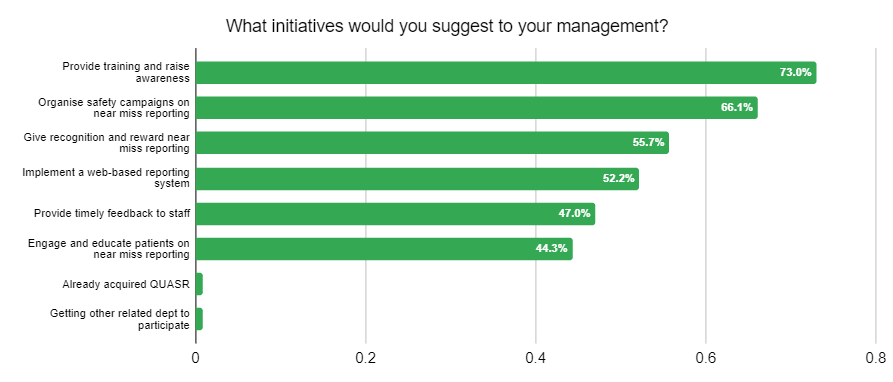
Respondents of our survey provided valuable insights and proposed initiatives for hospital management to enhance near miss reporting practices. Let’s delve into these suggestions, backed by results from the survey, and discuss their importance, benefits, and potential positive outcomes.
- Providing Training and Raising Awareness: The survey findings highlighted that a large majority of respondents (73.0%) suggested providing training and raising awareness about near miss reporting. Training programs equip healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills to identify and report near misses effectively. Raising awareness about the potential risks and benefits of reporting promotes a culture of vigilance and proactive risk management.
- Organizing Safety Campaigns: The survey results indicated that a significant majority of respondents (66.1%) recommended organizing safety campaigns dedicated to near miss reporting. Safety campaigns raise awareness, educate staff, and reinforce the significance of reporting near misses. These campaigns can include informative sessions, posters, interactive activities, and competitions to actively engage healthcare professionals in the reporting process.
- Giving Recognition and Rewards: A substantial number of respondents (55.7%) emphasized the importance of recognizing and rewarding near miss reporting efforts. Recognizing the contributions of staff who report near misses creates a positive and supportive environment. It motivates healthcare professionals to actively engage in reporting and fosters a sense of pride and ownership in patient safety.
- Implementing a Web-Based Reporting System: The survey highlighted that a significant percentage of respondents (52.2%) advocated for the implementation of a web-based reporting system. A web-based system offers advantages such as real-time reporting, streamlined processes, and data analysis capabilities. It facilitates efficient reporting, enhances data accuracy, and enables prompt identification of trends and patterns for targeted interventions.
- Providing Timely Feedback to Staff: The survey results showed that a majority of respondents (47.0%) suggested providing timely feedback to staff as an essential initiative. Timely feedback acknowledges the efforts of healthcare professionals, reinforcing the value of reporting and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. It builds trust and accountability while encouraging staff to remain engaged in near miss reporting.
- Engaging and Educating Patients on Near Miss Reporting: A significant number of respondents (44.3%) emphasized the importance of engaging and educating patients in near miss reporting. By involving patients, healthcare organizations empower them to actively participate in their own safety and contribute valuable insights. This collaborative approach strengthens the reporting culture and promotes transparency in healthcare.
- Getting Other Related Departments to Participate: The survey revealed that a small percentage (0.9%) of respondents suggested involving other related departments in near miss reporting. Collaborating with departments can provide a comprehensive understanding of near misses and facilitate a multidisciplinary approach to patient safety.
Implementing these initiatives based on the survey feedback can yield several positive outcomes for healthcare organizations. Enhanced near miss reporting improves patient safety by identifying and mitigating risks. It fosters a culture of continuous learning, empowers patients as active partners in their care, and strengthens the engagement and morale of healthcare professionals.
By embracing these proposed initiatives, hospital management can build a robust near miss reporting culture that prioritizes patient safety and cultivates a sense of shared responsibility among staff.
Current Near Miss Reporting Processes
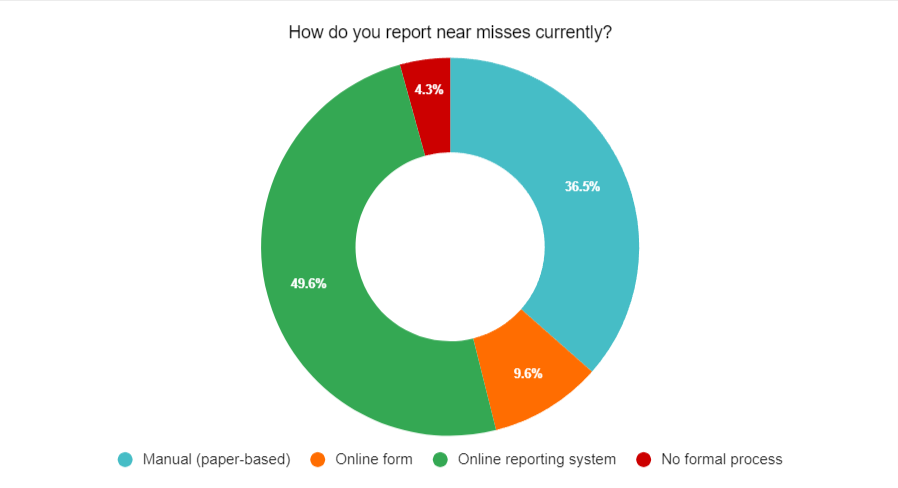
Let’s delve into the current methods used for near miss reporting based on the QUASR survey findings. Understanding these methods and their pros and cons is crucial for identifying areas of improvement and implementing more efficient reporting systems.
The survey revealed that hospitals employ various approaches for near miss reporting, including manual (paper-based) reporting, online forms, online reporting systems, and the absence of a formal reporting process.
- Manual (Paper-based) Reporting: Approximately 36.5% of respondents indicated that their hospitals still rely on manual reporting using paper-based forms. This traditional approach involves filling out physical forms and submitting them to the designated department. While this method may be familiar to some healthcare professionals, it has several drawbacks. Paper-based reporting can be time-consuming, prone to errors, and challenging to track and analyze. Additionally, it may hinder real-time reporting and timely response to near misses.
- Online Forms: A small portion of respondents (9.6%) mentioned using online forms for near miss reporting. Online forms offer the advantage of digitizing the reporting process, making it more accessible and convenient for healthcare professionals. However, they may still have limitations in terms of data analysis, tracking, and overall efficiency compared to more advanced online reporting systems.
- Online Reporting Systems: The majority of respondents (49.6%) reported using online reporting systems for near miss reporting. These systems provide a structured platform for capturing near miss incidents, allowing healthcare professionals to enter data electronically and submit reports securely. Online reporting systems offer benefits such as real-time data collection, automatic tracking, and easier data analysis. They enable organizations to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement more effectively. However, it is important to ensure that the online reporting system is user-friendly and intuitive to encourage widespread adoption and utilization.
- Absence of a Formal Reporting Process: It was concerning to note that a small percentage (4.3%) of respondents reported the absence of a formal near miss reporting process in their hospitals. Without a standardized reporting process, the identification and reporting of near misses may be inconsistent or overlooked entirely. This lack of formalization can hinder proactive risk management and the implementation of preventive measures.
Analyzing the different reporting methods underscores the need for more efficient and user-friendly systems. While manual reporting and online forms have their limitations, online reporting systems offer significant advantages in terms of real-time reporting, data analysis, and tracking. Implementing an advanced online reporting system can streamline the reporting process, enhance data accuracy, and facilitate prompt action to mitigate risks.
Survey Results Overview
The survey yielded several noteworthy findings regarding near miss reporting in healthcare settings:
- High Awareness Levels: The survey revealed that a significant percentage of respondents (25.2%) rated the awareness on near miss reporting in their hospitals as the highest level (5). This indicates a commendable level of awareness and recognition of the importance of near miss reporting.
- Major Barriers: The survey identified the major barriers to near miss reporting as heavy workload and time constraints, with a staggering 64.3% of respondents acknowledging this challenge. Additionally, 51.3% of respondents cited fear of punitive actions as another significant barrier. These statistics highlight the real obstacles faced by healthcare professionals when it comes to reporting near misses.
- Suggested Initiatives: The survey provided valuable insights into the initiatives that respondents believe would encourage near miss reporting. An overwhelming majority (73.0%) suggested providing training and raising awareness among staff, recognizing the importance of education in fostering a reporting culture. Furthermore, 66.1% emphasized the need for organizing safety campaigns to promote near miss reporting. Implementing a web-based reporting system was also favored by 52.2% of respondents, recognizing the potential benefits of a more streamlined and accessible reporting platform.
- Current Near Miss Reporting Methods: The survey revealed that 36.5% of respondents still rely on manual, paper-based reporting systems, while approximately 9.6% use online forms for near miss reporting. In contrast, the majority (49.6%) prefer online reporting systems for their real-time capabilities and data analysis features. However, it is concerning that 4.3% of respondents reported the absence of a formal near miss reporting process in their hospitals.
Implementing a Web-Based Reporting System
An online near miss reporting system offers several advantages when it comes to near miss reporting in healthcare organizations. Here are some key benefits and steps to implementation:
- Reducing Staff Workload: A web-based reporting system streamlines the reporting process by eliminating the need for manual paperwork and repetitive data entry. This automation significantly reduces staff workload, allowing them to focus more on patient care.
- Improving Productivity: With a web-based system, near misses can be reported in real-time, ensuring timely identification and documentation. This improves overall productivity as near misses are captured efficiently, enabling swift analysis and action.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: Web-based reporting systems enable the collection of data in real-time, providing immediate access to near miss reports. This facilitates prompt analysis, allowing healthcare organizations to identify trends or patterns in near misses and proactively address potential risks.
- Timely Identification of Trends: By analyzing near miss data in real-time, healthcare organizations can identify recurring issues or trends. This insight enables targeted interventions and process improvements to mitigate risks, ultimately enhancing patient safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our survey shed light on the current state of near miss reporting in Malaysia’s healthcare sector. The findings highlighted the high awareness levels among respondents, but also the presence of significant barriers such as heavy workload and fear of punitive actions. It is crucial for healthcare organizations to address these barriers and foster a culture of safety that encourages near miss reporting.
Initiatives such as training, safety campaigns, recognition and rewards, and the implementation of web-based reporting systems emerged as valuable solutions to improve near miss reporting practices. These initiatives can contribute to increased awareness, timely identification of near misses, and proactive risk mitigation.
It is essential for healthcare organizations to prioritize near miss reporting and actively work towards enhancing patient safety. By implementing the suggested initiatives and overcoming the identified barriers, healthcare professionals can create a safer environment for patients and continually improve the quality of care provided.
QUASR is a cloud-based, user-friendly, and secure incident and near miss reporting system.






