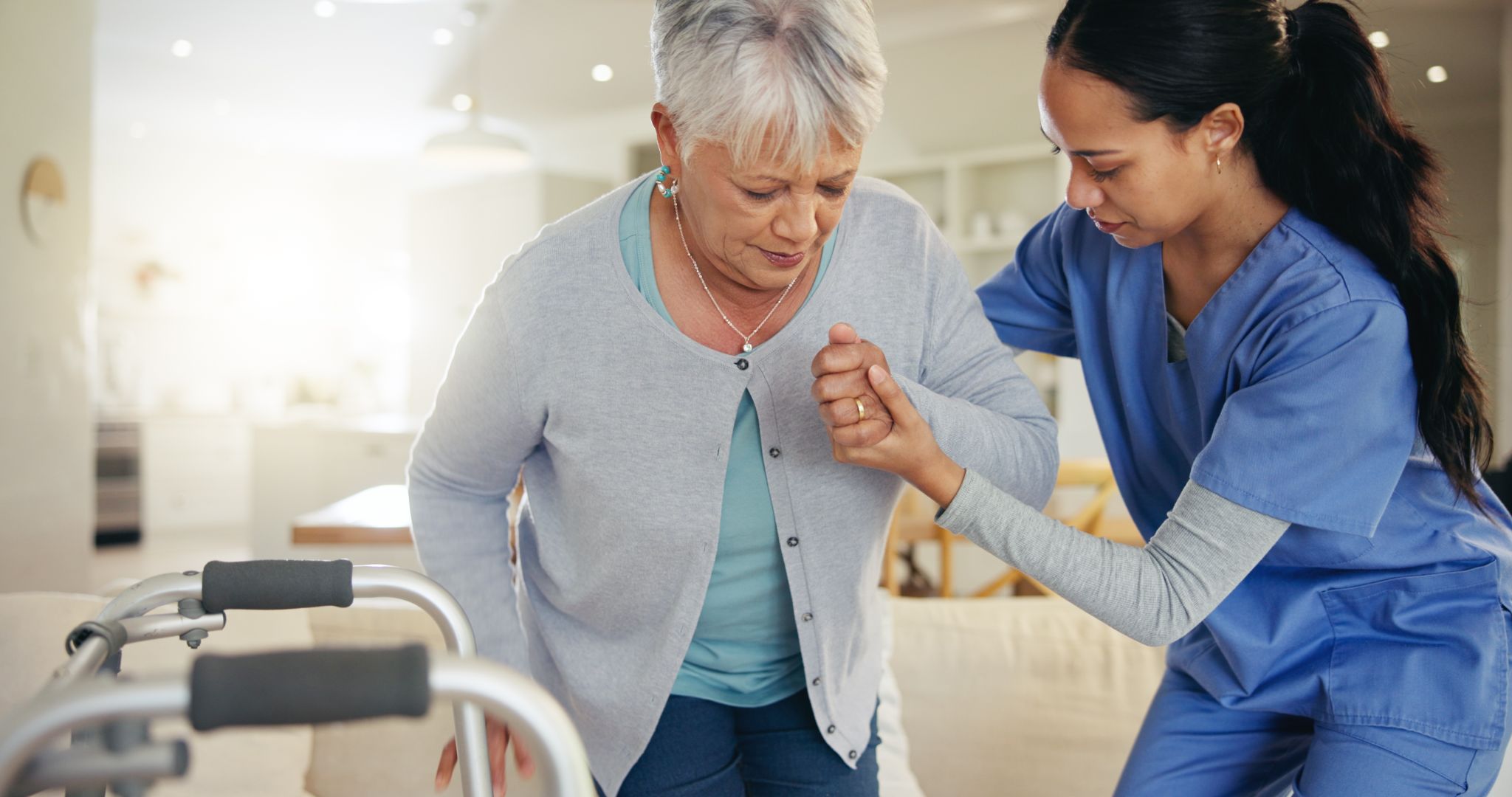

Leveraging Technology to Meet Incident Reporting Requirements under the New Aged Care Act in Australia
The new Aged Care Act, set to take effect on July 1, 2025, introduces sweeping reforms designed to enhance the

The new Aged Care Act, set to take effect on July 1, 2025, introduces sweeping reforms designed to enhance the
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) holds tremendous potential to transform the healthcare industry. Healthcare organizations are increasingly adopting AI

What is Proactive Risk Assessment? Proactive risk assessment (PRA) is a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential hazards
Needlestick and sharps injury (NSI) is a serious occupational hazard and health concern. Healthcare workers (HCWs) who have frequent exposure to needles are at increased risk of NSIs. Sharps exposures can lead to serious or fatal infections with bloodborne pathogens such as hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, or HIV. Proper reporting and prevention strategies are crucial in mitigating these risks.

AI-enabled health technologies soared from 5th in 2024 to the top of ECRI’s annual top 10 health technology hazards for 2025. This jump in ranking underscores the growing concerns over AI’s potential for misuse and oversight challenges, as its adoption accelerates across the healthcare sector. Unmet technology support needs for home care patients and tech vendor risk and cybersecurity threats make up the top three hazards.

Healthcare workers are at higher risk for workplace injury and illness compared to those working in construction, manufacturing, or transportation sectors.

Near miss reporting is crucial in improving patient safety and preventing harm. It helps in early detection of potential risks and hazards, improves safety culture and awareness, and promotes transparency and accountability.

The effectiveness of RCA can be undermined by common mistakes during the RCA process. Here are five common mistakes to avoid.

There are different ways to categorize incidents in healthcare settings. Incident categorization can be based on various criteria such as risk, severity, impact on patients, urgency, stage/process, and the nature or consequence of incidents. There are industry guidelines on categorizing or rating incidents for specific incident types.
Falls occur at all ages but are common among older people. According to some studies, falls occur in 30% of adults aged over 65 annually. Falls are a common reason that older people are admitted to hospital.